Redeam's Notifications API alerts you to changes based on configured rules. You will only receive notifications for the specific services you have registered for via Notification Registry. Notifications are sent via HTTP POST requests and cover the following event types:
- Channel Bindings
- Supplier Updates
- Product Updates
- Rate Updates
- Availability Changes
- Price Schedule Changes
- Booking Cancellations
Each notification contains key identifiers (e.g., supplierID, productID, operation) to help trigger the appropriate API requests.
API Calls in response to API Notifications
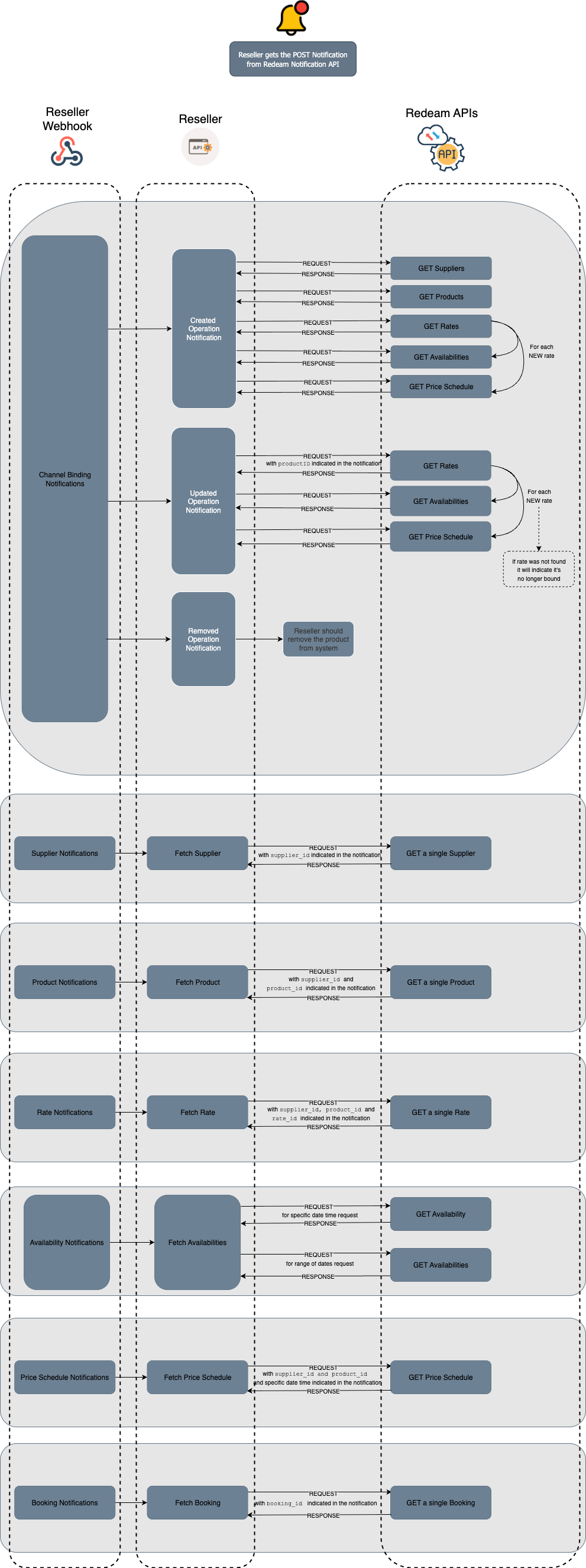
When a notification is received, determine the change type (operation) and make the relevant API calls to synchronize your system. Use the provided identifiers to retrieve updated data. The following table summarises the API endpoint calls for each notification type, as described in the diagram above.
| NOTIFICATION TYPE | API CALLS IN RESPONSE TO API NOTIFICATIONS |
|---|---|
| Channel Bindings | GET Suppliers, GET Products, GET Rates, GET Availabilities, GET Price Schedule |
| Supplier | GET a single Supplier |
| Product | GET a single Product |
| Rate | GET a single Rate |
| Availability | GET Availabilities and / or GET a single Availability |
| Price Schedule | GET Price Schedule |
| Booking | GET a single Booking |
Channel Binding Notifications
Channel binding notifications cover any changes related to the bindings that are connected to you, the Reseller, which can include both Product and Rate levels. In other words, notifications are triggered by changes at either level - whether it's a Product or the associated Rate that has been updated. However, the notification itself typically only includes the Product information. This is because, in practice, Products are the primary reference point when looking up changes, and Rate adjustments are tied to the Products they belong to. Therefore, the notification may not explicitly detail Rate changes, but they are still relevant and part of the binding process.
Receive a Channel Binding Notification when one of the below operations is performed:
created- Triggered when a new binding is established at the Product level. This could be the first Rate being bound or when the entire Product is newly bound.updated- Triggered when changes are made to bound Products and Rates, such as Rate-level adjustments within an already-bound Product.- You already have a Product (e.g., a tour or experience) bound to your system. Later the Supplier adds a new Rate (like “Early Bird” or “VIP”) under that Product. Since this new Rate becomes part of the existing binding, Redeam will send an
updatedchannel binding notification to reflect that change.
- You already have a Product (e.g., a tour or experience) bound to your system. Later the Supplier adds a new Rate (like “Early Bird” or “VIP”) under that Product. Since this new Rate becomes part of the existing binding, Redeam will send an
removed- Triggered when the entire binding is removed. Only happens when it is removed in full, the Product and all the Rates under it.
Note: At this time, any Rate changes, whether a Rate was created or removed, will always register as an update event as the Rate object is associated to a Product and it's data. This is not a pricing change.
Note neither rateID nor the start and end dates are part of the notification body here but the operation field is present. In this case, you will get the notification with the details to identify the corresponding changes.
If it is a created case, you should call all sets of Redeam's APIs to sync the data in your system, this includes GET Suppliers, GET Products, GET Rates, GET Availabilities and GET Price Schedule.
If it is a removed case you should remove that Product from your system.
If it is an updated case you should consider:
- Call Get Rates with the corresponding Product ID from the notification
- Iterate through those Rates to compare them with the ones connected in your system
- For each NEW Rate call GET Availabilities and GET Price Schedule
- For each already known Rate, no action is needed
- If a Rate is missing, it will indicate it's no longer bound
- Note: At this time, any Rate changes, whether a Rate was
createdorremoved,will always register as anupdateevent as the Rate object is associated to a Product and it's data.
- Note: At this time, any Rate changes, whether a Rate was
Identifiers:
supplierID- the unique identifier of the Supplier, as used in the Booking/Reseller APIs.productID- the unique identifier of the Product, as used in the Booking/Reseller APIs.operation-created,removedorupdated.sum- a secure SHA256 HMAC checksum (in hexadecimal format) used to verify the authenticity of the notification. To validate it, generate a checksum using thetimestamp,token, and yoursecurity_key. If your result matches thesum, the notification is considered authentic and untampered.timestamp- unix timestamp of when the signature was generated.token- a unique authentication token for this message. It’s used along with thetimestampand yoursecurity_keyto generate and validate thesum(checksum), ensuring the notification's authenticity.
💡 Recommendation: Use the Channel Binding Test Notification Endpoint to safely simulate binding notifications without affecting production data.
{ "supplierID": "65cddcad-b3e0-4fd9-a466-7188104742a2", "productID": "65cddcad-b3e0-4fd9-a466-7188104742a2", "operation": "created", "signature": { "sum": "e2885631a81ed00ad9606a0a6ce2f1efdcf355a9785e0dc1ff027b039a95c820", "timestamp": 1727715823, "token": "2915c9b2-9cd9-4baf-b5b7-79d95ea3eb2c" }}Supplier Notifications
When receiving supplier-related notifications, the alert message will inform you of updates to Supplier details bound to your system, such as changes to Supplier contact information. Currently, only the updated operation type is supported for Supplier notifications, meaning you will receive alerts when existing Supplier data is modified. For more information please refer to Supplier Notifications API documentation.
The notification will include the supplierID, which you can use to identify the corresponding changes. Use this ID to make the appropriate Supplier API request.
Identifiers:
supplierID- the unique identifier of the Supplier, as used in the Booking/Reseller APIs.productID- the unique identifier of the Product, as used in the Booking/Reseller APIs.operation-updated(this is the only operation currently supported for this type of notification).sum- a secure SHA256 HMAC checksum (in hexadecimal format) used to verify the authenticity of the notification. To validate it, generate a checksum using thetimestamp,token, and yoursecurity_key. If your result matches thesum, the notification is considered authentic and untampered.timestamp- unix timestamp of when the signature was generated.token- a unique authentication token for this message. It’s used along with thetimestampand yoursecurity_keyto generate and validate thesum(checksum), ensuring the notification's authenticity.
Note: The Supplier Test Notification Endpoint allows you to simulate Supplier notifications without impacting production data.
💡 Recommendation: Use the Supplier Test Notification Endpoint to safely simulate Supplier notifications without affecting production data.
{ "supplierID": "65cddcad-b3e0-4fd9-a466-7188104742a2", "operation": "updated", "signature": { "sum": "e2885631a81ed00ad9606a0a6ce2f1efdcf355a9785e0dc1ff027b039a95c820", "timestamp": 1727715823, "token": "2915c9b2-9cd9-4baf-b5b7-79d95ea3eb2c" }}Since Supplier visibility is managed through channel bindings, Channel Bindings Notifications are the primary source for tracking newly accessible Suppliers.
Product Notifications
Product Notifications will alert you about changes to Product data, such as updates to descriptions, hours, or location details. Currently, only the updated operation type is available, so notifications will be triggered whenever Product information is modified.
The notification will contain the supplierID and productID, allowing you to track the relevant changes. Use these IDs to make the necessary Product API request.
Identifiers:
supplierID- the unique identifier of the Supplier, as used in the Booking/Reseller APIs.productID- the unique identifier of the Product, as used in the Booking/Reseller APIs.operation-updated(this is the only operation currently supported for this type of notification).sum- a secure SHA256 HMAC checksum (in hexadecimal format) used to verify the authenticity of the notification. To validate it, generate a checksum using thetimestamp,token, and yoursecurity_key. If your result matches thesum, the notification is considered authentic and untampered.timestamp- unix timestamp of when the signature was generated.token- a unique authentication token for this message. It’s used along with thetimestampand yoursecurity_keyto generate and validate thesum(checksum), ensuring the notification's authenticity.
💡 Recommendation: Use the Product Test Notification Endpoint to safely simulate Product notifications without affecting production data.
{ "supplierID": "65cddcad-b3e0-4fd9-a466-7188104742a2", "productID": "65cddcad-b3e0-4fd9-a466-7188104742a2", "operation": "updated", "signature": { "sum": "e2885631a81ed00ad9606a0a6ce2f1efdcf355a9785e0dc1ff027b039a95c820", "timestamp": 1727715823, "token": "2915c9b2-9cd9-4baf-b5b7-79d95ea3eb2c" }}Using both Product Notifications and Channel Bindings Notifications ensures full visibility into Product availability and updates within your system.
Rate Notifications
Rate Notifications inform you about updates to Rate details, such as cancel, holdable, hours and traveler conditions. At this time, only the updated operation type is supported, meaning alerts are triggered whenever existing Rate information is modified.
The notification will include the supplierID, productID and rateID, enabling you to track relevant changes. Use these IDs to make the appropriate Rate API request.
Identifiers:
supplierID- the unique identifier of the Supplier, as used in the Booking/Reseller APIs.productID- the unique identifier of the Product, as used in the Booking/Reseller APIs.rateID- the unique identifier of the Rate, as used in the Booking/Reseller APIs.operation-updated(this is the only operation currently supported for this type of notification).sum- a secure SHA256 HMAC checksum (in hexadecimal format) used to verify the authenticity of the notification. To validate it, generate a checksum using thetimestamp,token, and yoursecurity_key. If your result matches thesum, the notification is considered authentic and untampered.timestamp- unix timestamp of when the signature was generated.token- a unique authentication token for this message. It’s used along with thetimestampand yoursecurity_keyto generate and validate thesum(checksum), ensuring the notification's authenticity.
💡 Recommendation: Use the Rate Test Notification Endpoint to safely simulate Rate notifications without affecting production data.
{ "supplierID": "65cddcad-b3e0-4fd9-a466-7188104742a2", "productID": "65cddcad-b3e0-4fd9-a466-7188104742a2", "rateID": "65cddcad-b3e0-4fd9-a466-7188104742a2", "operation": "updated", "signature": { "sum": "e2885631a81ed00ad9606a0a6ce2f1efdcf355a9785e0dc1ff027b039a95c820", "timestamp": 1727715823, "token": "2915c9b2-9cd9-4baf-b5b7-79d95ea3eb2c" }}Using both Rate Notifications and Channel Bindings Notifications ensures full visibility into Rate availability and updates within your system.
Availability Notifications
Receive an Availability Notification when Availability data changes.
Availability Notification are not sent for all changes, these notifications are triggered based on the thresholds set during rule configuration Notification Registry (e.g., maxLookAheadDays, vacanciesUnder).
The availability information is primarily forwarded as received from supplier systems without modification. Consequently, the handling of this data can vary based on its original format when provided to Redeam; it may consist of either individual notifications or multiple notifications for each day. Therefore, you have the option to either Retrieve a list of availabilities or Retrieve a single availability.
Note in the notification you will get the supplierID, productID, rateID and start and end date to identify the corresponding changes and use those details to make the appropriate API call(s).
Identifiers:
supplierID- the unique identifier of the Supplier, as used in the Booking/Reseller APIs.productID- the unique identifier of the Product, as used in the Booking/Reseller APIs.rateID- the unique identifier of the Rate, as used in the Booking/Reseller APIs.start– the start of the date range (in RFC-3339 format) for which availability data has changed. Used to narrow down what should be fetched via GET endpoints.end– the end of the date range (in RFC-3339 format) for which availability data has changed. Used to define the full time window impacted by the update.sum- a secure SHA256 HMAC checksum (in hexadecimal format) used to verify the authenticity of the notification. To validate it, generate a checksum using thetimestamp,token, and yoursecurity_key. If your result matches thesum, the notification is considered authentic and untampered.timestamp- unix timestamp of when the signature was generated.token- a unique authentication token for this message. It’s used along with thetimestampand yoursecurity_keyto generate and validate thesum(checksum), ensuring the notification's authenticity.
💡 Recommendation: Use the Availability Test Notification Endpoint to safely simulate availability notifications without affecting production data.
{ "supplierID": "65cddcad-b3e0-4fd9-a466-7188104742a2", "productID": "65cddcad-b3e0-4fd9-a466-7188104742a2", "rateID": "65cddcad-b3e0-4fd9-a466-7188104742a2", "start": "2024-09-30T11:57:16Z05:00", "end": "2024-09-30T11:57:16Z05:00", "signature": { "sum": "e2885631a81ed00ad9606a0a6ce2f1efdcf355a9785e0dc1ff027b039a95c820", "timestamp": 1727715823, "token": "2915c9b2-9cd9-4baf-b5b7-79d95ea3eb2c" }}Price Schedule Notifications
Receive a Price Schedule Notification when Pricing data changes.
In the notification you will get the supplierID, productID and start and end date information. Note, in this case, the rateID is not part of the notification body but with the other details you are still able to identify the corresponding changes and use those details to make the appropriate GET Price Schedule API call.
Identifiers:
supplierID- the unique identifier of the Supplier, as used in the Booking/Reseller APIs.productID- the unique identifier of the Product, as used in the Booking/Reseller APIs.start– the start of the date range (in RFC-3339 format) for which price data has changed. Used to narrow down what should be fetched via GET endpoints.end– the end of the date range (in RFC-3339 format) for which price data has changed. Used to define the full time window impacted by the update.sum- a secure SHA256 HMAC checksum (in hexadecimal format) used to verify the authenticity of the notification. To validate it, generate a checksum using thetimestamp,token, and yoursecurity_key. If your result matches thesum, the notification is considered authentic and untampered.timestamp- unix timestamp of when the signature was generated.token- a unique authentication token for this message. It’s used along with thetimestampand yoursecurity_keyto generate and validate thesum(checksum), ensuring the notification's authenticity.
💡 Recommendation: Use the Price Schedule Test Notification Endpoint to safely simulate price schedule notifications without affecting production data.
{ "supplierID": "65cddcad-b3e0-4fd9-a466-7188104742a2", "productID": "65cddcad-b3e0-4fd9-a466-7188104742a2", "start": "2024-09-30T11:57:16Z05:00", "end": "2024-09-30T11:57:16Z05:00", "signature": { "sum": "e2885631a81ed00ad9606a0a6ce2f1efdcf355a9785e0dc1ff027b039a95c820", "timestamp": 1727715823, "token": "2915c9b2-9cd9-4baf-b5b7-79d95ea3eb2c" }}Booking Notifications
Booking Notifications inform you of booking-related events, such as cancellations or confirmation of tickets attached to confirmed bookings - applicable only when 202 responses are supported. These notifications allow you to stay in sync with the booking status.
Currently, the following operation types are supported:
canceled– Triggered when a booking has been canceled.tickets-added– Triggered when tickets are confirmed after a booking was initially accepted with a202response. This is useful for detecting when tickets have actually been generated and associated with a booking.
When a tickets-added notification is received, your system should treat it as a confirmation that the booking is finalised and tickets are now available for retrieval. This typically follows an earlier 202 Accepted response from the Booking API.
Identifiers
bookingID– the unique identifier assigned by Redeam for the booking.startTime– the scheduled start time of the booking.resellerBookingReference– the reseller reference ID, used by the Booking API partner to provide your own reference for the booking.operation–canceledortickets-addedsum- a secure SHA256 HMAC checksum (in hexadecimal format) used to verify the authenticity of the notification. To validate it, generate a checksum using thetimestamp,token, and yoursecurity_key. If your result matches thesum, the notification is considered authentic and untampered.timestamp- unix timestamp of when the signature was generated.token- a unique authentication token for this message. It’s used along with thetimestampand yoursecurity_keyto generate and validate thesum(checksum), ensuring the notification's authenticity.
💡 Recommendation: Use the Booking Test Notification Endpoint to safely simulate booking notifications without affecting production data.
{ "bookingID": "65cddcad-b3e0-4fd9-a466-7188104742a2", "startTime": "2024-01-18T10:05:15Z", "resellerBookingReference": "BR0987654321", "operation": "canceled", "signature": { "sum": "e2885631a81ed00ad9606a0a6ce2f1efdcf355a9785e0dc1ff027b039a95c820", "timestamp": 1727715823, "token": "2915c9b2-9cd9-4baf-b5b7-79d95ea3eb2c" }}Testing Notifications with Redeam's Test Endpoints
Redeam provides dedicated test endpoints for safely simulating notification events without impacting live data. These endpoints allow you to validate your webhook integrations for booking, event, and other notifications before going live.
🔗 See Redeam’s Test Endpoints for full details and usage instructions.
For more details about each endpoint and their schema please check the Redeam Notifications API documentation.